Table of contents
In Javascript, there are three properties that can be used to set or return an HTML element's content in the DOM: innerHTML, innerText, and textContent.
Sometimes it becomes very confusing which one to use, so in this post I break down the subtle differences between innerHTML, innerText, and textContent when you’re manipulating your JavaScript code.
Let's start with some sample HTML code.
<p id="demo">This p tag contains lot of spaces
<span style="visibility: hidden;">& a hidden text</span>.</p>
Let’s say we’re creating a variable demoP and set it equal to our p tag.
var demoP = document.querySelector("#demo");
console.log(demoP.innerHTML);
console.log(demoP.innerText);
console.log(demoP.textContent);
Now, I’ll explain what you get when you call innerHTML, innerText and textContent on that demoP variable.
.innerHTML
The innerHTML property sets and returns the content of an element with new HTML content.
innerHTML returns the string inside our p tag and the HTML markup contained within our string, including any spacing, line breaks, etc.
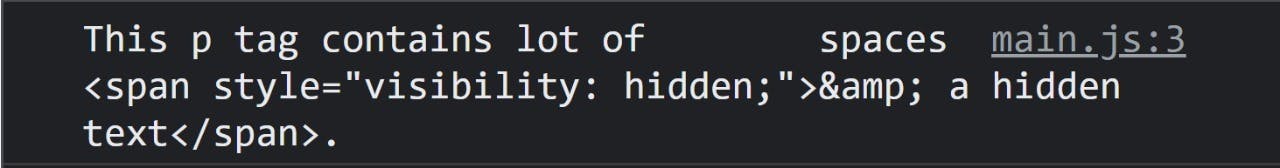
If the text inside the element includes the characters &, <, or >, innerHTML will return these characters as HTML entities &, <, and >.
.innerText
The innerText property returns the content of all elements, except for <script> and <style> elements.
When you only need to see what’s in the element with zero formatting, you have to use innerText.

.textContent
The textContent property returns the raw content with styling inside of all elements, but excludes the HTML element tags. This includes <script> and <style> elements, whitespace, line breaks, and carriage returns.
When you want to see what’s in the element, plus any styling on it, you can use textContent.

Note: Unlike innerHTML, textContent has better performance because its value is not parsed as HTML. For that reason, using textContent can also prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks. Unlike innerText, textContent isn't aware of CSS styling and will not trigger a reflow. All Node objects have textContent, whereas only HTML Element objects have innerText.
Hope this post guide you when to use innerHTML, innerText and textContent in your JavaScript code.
If you liked my content, connect with me? 😃

